Edu- World is one of the largest and best education service providers in India with its head office in Mangalore and numerous branches across the world. Founded in 2001 with a core vision to guide the students through a journey of knowledge and success. Edu world is now the most trusted and highly rated Educational Consultant in South India.
In 2015 we expanded our reach towards American Continent with our office located at Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. We are exclusively concentrating on the American sector so that we could deliver the best for our customers through our Canadian office unlike any other competitors in the field.
Why US?
We are Unique in what we do unlike others in the market because we do listen first to what the customer has to say and then propose the best option that is available for his brightest future. As we believe in verbal publicity from a happy customer that lasts longer.
Edu World Canada operates from Vancouver, western Canada. We offer wide and unique range of courses with end to end support & services starting form from Course/College and Admission processes for all leading educational institutions in Canada and Caribbean Islands.

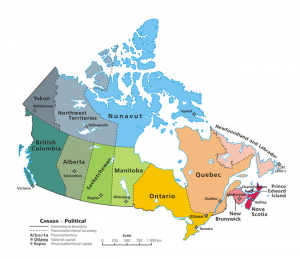
CANADA
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Canada:
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west and northward into the Arctic Ocean. It is the world's second largest country by total area, and shares land borders with the United States to the south and northwest, and marine borders with France and Greenland on the east and northeast, respectively.
The lands have been inhabited for millennia by various groups of aboriginal peoples. Beginning in the late 15th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled the Atlantic coast. France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763 after the Seven Years' War. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of additional provinces and territories and a process of increasing autonomy from the United Kingdom, highlighted by the Statute of Westminster in 1931 and culminating in the Canada Act in 1982 which severed the vestiges of legal dependence on the British parliament.
Canada is a federation that is governed as a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy with Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state. It is a bilingual and multicultural country, with both English and French as official languages at the federal level. Technologically advanced and industrialized, Canada maintains a diversified economy that is heavily reliant upon its abundant natural resources and upon trade—particularly with the United States, with which Canada has a long and complex relationship.
Population is 33,476,688 people (2011 Census)
Climate of Canada
The average maximum/minimum temperatures of Canada of various cities across Canada, based on the climate period from 1981-2010 for the months of January and July (generally the lowest/highest average temperature months, but not in every case).
The major Canadian city that falls outside the continental climate schema is Vancouver, which experiences an oceanic climate with a marked summer dry season. Of the eight largest Canadian cities, Ottawa, Montreal and Toronto have the warmest summers, Winnipeg the coldest winters, while Vancouver's winters are far milder than any other large city in Canada.
Central and northern Canada experiences subarctic and Arctic climates, much of them arid. Those areas are not heavily populated due to the severe climate, where it drops below −20 °C (−4 °F) on most winter days and has a very brief summer season.
Climate of British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost province of Canada, bordered by the Pacific Ocean. With an area of 944,735 square kilometres (364,764 sq mi) it is Canada's third-largest province. The province is almost four times the size of Great Britain, two and one-half times larger than Japan and larger than every U.S. state except Alaska. It is bounded on the northwest by the U.S. state of Alaska, directly north by Yukon and the Northwest Territories, on the east by Alberta, and on the south by the U.S. states of Washington, Idaho, and Montana. Formerly part of the British Empire, the southern border of British Columbia was established by the 1846 Oregon Treaty. The province is dominated by mountain ranges, among them the Canadian Rockies but dominantly the Coast Mountains, Cassiar Mountains, and the Columbia Mountains. Most of the population is concentrated on the Pacific coast, notably in the area of Vancouver, located on the southwestern tip of the mainland, which is known as the Lower Mainland.
Summer daytime temperatures in the Southwestern Interior are the hottest in Canada. During July and August, the average daily maximum temperature around Osoyoos and Spences Bridge is over 29 °C (84.2 °F), though Lillooet and Lytton erroneously claim to be hotter and vie for the title of "Canada's Hot Spot". This is because their summertime temperature extremes tend to be hotter than Osoyoos and Spences Bridge (despite a slightly cooler average temperature). This heat combined with little precipitation means that arid animals and vegetation thrive. Although winter temperatures are much colder than Coastal British Columbia, this area is still milder than almost anywhere else in Canada. Southern Interior valleys, including the Okanagan Valley, are spared the incessant precipitation found on the coast, but they receive some of the lowest amounts of bright sunshine in Canada during the winter months. This is a result of winter temperature inversions that leave the valleys in a layer of thick cloud while the rest of the province basks in sunshine.
Economy of B.C
British Columbia has a history of being a resource dominated economy, centred on the forestry industry but also with fluctuating importance in mining. Employment in the resource sector has fallen steadily as a percentage of employment, and new jobs are mostly in the construction and retail/service sectors. It now has the highest percentage of service industry jobs in the west, comprising 72% of British Columbia has a history of being a resource dominated economy, centred on the forestry industry but also with fluctuating importance in mining. Employment in the resource sector has fallen steadily as a percentage of employment, and new jobs are mostly in the construction and retail/service sectors. It now has the highest percentage of service industry jobs in the west, comprising 72% of industry (compared to 60% Western Canadian average).The largest section of this employment is in finance, insurance, real estate and corporate management. Many areas outside of metropolitan areas, however, are still heavily reliant on resource extraction. With its film industry known as Hollywood North, the Vancouver region is the third-largest feature film production location in North America, after Los Angeles and New York City.
British Columbia's GDP is the fourth largest in Canada at C$219.99 billion in 2012. GDP per capita was $45,430.[56] British Columbia's debt was $57 billion in June 2013, or 25.9% of GDP.
International Students
The total number of international (foreign-born) students in British Columbia for the year of 2006 was 44,799, up from 23,011 in 1997.[37] This does not include students enrolled in programs of less than six months. This seems contradictory to the statistic of “more than 140,000 international students choosing to study in British Columbia each year” the British Columbia government claims in its Campus 2020: Thinking Ahead report. The top 10 source countries for long-term international students in 2003-2004 were: China, Japan, South Korea, United States, Taiwan, Hong Kong SAR, Indonesia, Mexico, India and the United Kingdom